Կարբոնային սևը գլոբալ արտադրության հիմնարար կազմածառայություն է, որը ձևավորվում է օրգանական հումքի վերահսկվող՝ անընդհատ այրման արդյունքում և առաջացնում է փոշիանման նյութ, որն ունի յուրահատուկ ֆիզիկական և քիմիական հատկություններ, որոնք այն անփոխարինելի են դարձնում տարբեր արդյունաբերական ոլորտներում: Այս նյութը գոյություն ունի ինչպես բնական, այնպես էլ սինթետիկ ձևերով, սակայն արդյունաբերական կիրառման համար գերակշռում է սինթետիկ կարբոնային սևը՝ պայմանավորված նրա հաստատուն որակով և հատուկ հատկություններով: Բնական կարբոնային սևը առաջանում է բնական գործընթացների արդյունքում, ինչպիսիք են անտառների հրդեհները կամ հրաբխային գործողությունները, սակայն այդ աղբյուրները չունեն արդյունաբերական կիրառման համար անհրաժեշտ համասեռությունը: Սինթետիկ կարբոնային սևի արտադրությունը ներառում է այրման պայմանների ճշգրիտ վերահսկողություն՝ կարգավորելով ջերմաստիճանը, վառելիքի տեսակը և օդի հոսքը՝ ստանալու համար հստակ չափսերի, մակերեսի և կառուցվածքի մասնիկներ: Այդ կարգավորումները թույլ են տալիս արտադրողներին կարբոնային սևը հարմարեցնել տարբեր վերջնական կիրառությունների ճշգրիտ պահանջներին՝ սկսած անվադողերի ռետինի ամրացումից մինչև ծածկույթների խորը գունավորում:


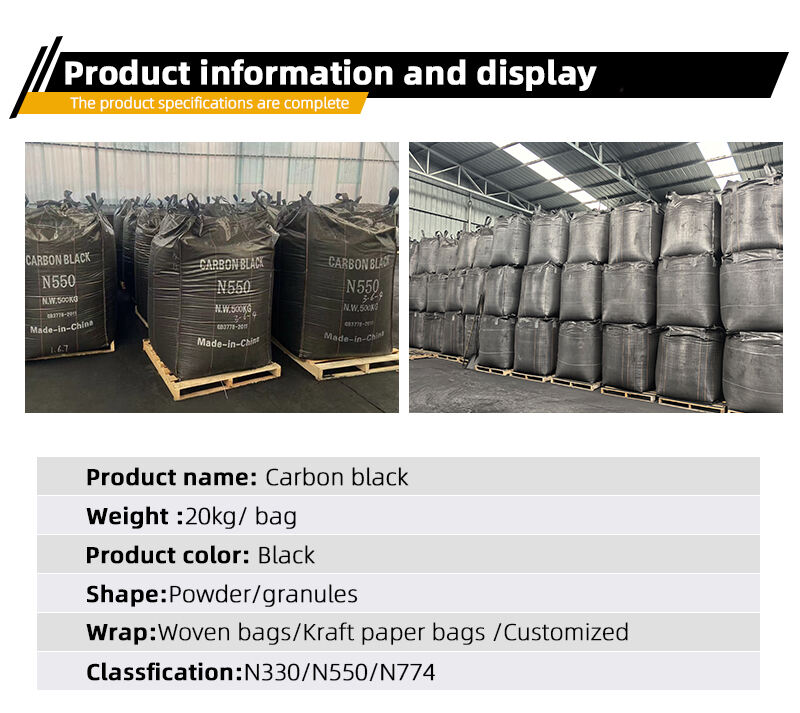
Ածխածնի սևի հիմնական առանձնահատկությունները կայանում են նրա բարձր մակերեսի մակերեսի, ծակոտկեն կառուցվածքի և ներքին հատկությունների մեջ, ինչպիսիք են երանգավորման ամրությունը, ամրացնող ունակությունը և հաղորդականությունը: Բարձր մակերեսը պայմանավորված է մասնիկների փոքր չափսերով, որոնք ստեղծում են մեծ շփման մակերես ածխածնի սևի և հիմնական նյութերի, ինչպիսիք են ռետինը կամ պլաստիկը, միջև: Այս շփումը հնարավորություն է տալիս ամուր կապակցել՝ բարելավելով կոմպոզիտային նյութերի ընդհանուր կատարողականը: Ծակոտկեն կառուցվածքը մեծացնում է կլանման ունակությունը, ինչը ածխածնի սևը դարձնում է օգտակար այնպիսի կիրառություններում, ինչպիսիք են ջրի մաքրումը կամ կատալիզատորային հենարանները, չնայած դրա հիմնական արդյունաբերական դերը կենտրոնացած է ամրացման և գունավորման վրա: Գունավորման ամրությունը վերաբերում է գույն հաղորդելու ունակությանը, որտեղ ածխածնի սևը տալիս է ինտենսիվ սև երանգներ, որոնք դիմադրում են ժամանակի ընթացքում մարելուն: Ամրացնող ունակությունը այն դարձնում է կարևոր ռետինե արտադրանքներում, որտեղ այն ամրացնում է ռետինե պոլիմերների մոլեկուլային կապերը՝ մեծացնելով ամրությունը և մաշվածության դիմադրությունը: Հաղորդականությունը, որը առկա է որոշակի տեսակների մեջ, թույլ է տալիս ածխածնի սևին ցրել ստատիկ էլեկտրականությունը, որը հիմնական առանձնահատկություն է էլեկտրոնիկայի պլաստիկ փաթեթավորման կամ արդյունաբերական խողովակների համար նախատեսված կիրառություններում:
Կաուչուկի արդյունաբերությունը ածխածնային սևուկի ամենախոշոր սպառողն է, որտեղ փողրիկների արտադրությունը պահանջարկի զգալի մասն է կազմում: Ածխածնային սևուկի ամրացնող հատկությունները կաուչուկը վերածում են տևական նյութի, որը կարող է դիմանալ ճանապարհների խիստ պայմաններին: Փողրիկների արտադրության ընթացքում փողրիկի տարբեր մասերը օգտագործում են ածխածնային սևուկի տարբեր սեղաններ՝ համապատասխանելով կոնկրետ շահարկման պահանջներին: Փողրիկների եզրագոտիները, որոնք ճանապարհի հետ շփման հիմնական բեռն են կրում, օգտագործում են ածխածնային սևուկի այն սեղանները, որոնք օպտիմալ են մաշվածության դիմաց պայքարի համար: Այդ սեղանները կաուչուկային պոլիմերների հետ կապեր են առաջացնում, նվազեցնում մաշվածությունը և երկարաձգում փողրիկների կյանքի տևողությունը: Շոֆերները շահում են ավելի երկար կյանք ունեցող փողրիկներից, որոնք պահպանում են կապող հատկությունները հազարավոր կիլոմետրներ շահարկման ընթացքում: Փողրիկների կողային մասերը, որոնք ճկունություն են պահանջում՝ ծռման և ձգման դիմաց կանգնելու համար, օգտագործում են ածխածնային սևուկի այն սեղանները, որոնք բարելավում են ճկունությունը՝ միաժամանակ ապահովելով UV պաշտպանություն: Առանց ածխածնային սևուկի կողային մասերը արագ կքայքայվեն արևի տակ, ինչը կհանգեցնի ճեղքերի և փողրիկների վաղաժամկետ անսարքության: Փողրիկների արմատուրաները, որոնք փողրիկի ներքին կառուցվածքն են և կրում են բեռը, օգտագործում են ածխածնային սևուկ՝ ամրությունը ամրացնելու համար, ապահովելով, որ փողրիկը կարողանա կրել ծանր բեռներ առանց դեֆորմացիայի: Փողրիկներից բացի, ածխածնային սևուկից կախված են նաև այլ կաուչուկե արտադրանքներ, ինչպիսիք են լարակալները, փականները, փոխադրող ժապավենները և խողովակները: Լարակալներն ու փականները օգտագործում են ածխածնային սևուկ՝ յուղերի և քիմիական նյութերի դիմադրությունը բարելավելու համար, ապահովելով դրանց ամբողջականությունը արդյունաբերական սարքավորումներում: Փոխադրող ժապավենները, որոնք օգտագործվում են հանքարդյունաբերության և արտադրության մեջ, հիմնված են ածխածնային սևուկի վրա՝ մաշվածության դիմադրության համար, որը թույլ է տալիս դիմակայել ծանր բեռներին և կոպտատեսակ նյութերին՝ առանց մաշվելու: Հեղուկներ կամ գազեր տեղափոխելու համար օգտագործվող խողովակները օգտագործում են ածխածնային սևուկ՝ ճկունությունն ու տևականությունը բարելավելու համար, կանխելով ճեղքերն ու կորուստները:
Պլաստմասսայի արդյունաբերությունը կարբոնային սևը օգտագործում է մի շարք գործառույթների համար, այդ թվում՝ ներկում, UV պաշտպանություն, հաղորդակցություն և ամրացում: Որպես ներկ, կարբոնային սևը պլաստմասսայի արտադրանքներին՝ ավտոմեքենաների ձևավորումից սկսած մինչև կենցաղային տեխնիկան, տալիս է համազանգված և ինտենսիվ սև գույն: Կարբոնային սևը պահպանում է գույնը նույնիսկ ծայրահեղ պայմաններում, ի տարբերություն օրգանական ներկերի, որոնք կարող են թուլանալ կամ թափվել, և դա այն դարձնում է իդեալական արտաքին տարածքներում օգտագործվող պլաստմասսայի արտադրանքների համար, ինչպիսիք են այգու ֆուրնիտուրան կամ շինարարական նյութերը: Մեկ այլ կարևոր դեր էլ UV պաշտպանությունն է. կարբոնային սևը կլանում է UV ճառագայթները, որոնք ժամանակի ընթացքում կարող են պլաստմասսան դարձնել փխրուն և գույնը փոխել: Օրինակ՝ արտաքին ջրատարներում օգտագործվող պլաստմասսայի խողովակները պարունակում են կարբոնային սև՝ արևի վնասակար ազդեցությունից պաշտպանվելու համար, որպեսզի տասնյակ տարիներ շարունակ մնան գործունակ: Հաղորդակցություն ունեցող կարբոնային սևի տեսակները օգտագործվում են պլաստմասսայի այն արտադրանքներում, որոնք պահանջում են ստատիկ էլեկտրականության ցրում, օրինակ՝ էլեկտրոնային մասերի փաթեթավորման համար: Այդ տեսակները պլաստմասսայի մեջ կառուցում են հաղորդակցության ցանց, որը անվտանգ կերպով շրջանցում է ստատիկ էլեկտրականությունը, որը կարող է վնասել զգայուն էլեկտրոնիկան: Պլաստմասսայի ամրացումը պողպատի համեմատությամբ ավելի քիչ է արտահայտված, սակայն կարբոնային սևը միևնույն է բարելավում է մեխանիկական հատկությունները, ինչպիսիք են ձգման ամրությունը և հարվածային դիմադրությունը: Օրինակ՝ ծանր ապրանքներ տեղափոխելու համար օգտագործվող պլաստմասսայի տուփերը պարունակում են կարբոնային սև՝ բեռնակրող ունակությունը մեծացնելու և կոտրվելու հավանականությունը նվազեցնելու համար:
Լիցքավորման արդյունաբերությունը կիստածխածնին է հենվում՝ ներկման ուժի, տևականության և ամպրոպակայունության համար: Մեքենաների, շինությունների և սարքավորումների պաշտպանության համար օգտագործվող արդյունաբերական լիցքավորումները կիստածխածին են ներառում՝ կոռոզիայի դիմադրություն և UV պաշտպանություն ապահովելու համար: Արտաքին գործոններին կամ կորոզիոն քիմիկատներին ենթարկվող գործարանային սարքավորումները շահում են կիստածխածնով լիցքավորումներից, քանի որ նյութը ստեղծում է խոչընդոտ, որը կանխում է ժանգոտումն ու քայքայումը: Ճարտարապետական լիցքավորումները, ներառյալ արտաքին և ներքին ներկերը, կիստածխածին են օգտագործում՝ խորը, երկարակյաց սև և մոխրագույն երանգներ ստանալու համար: Կիստածխածնով արտաքին տան ներկերը պահպանում են իրենց գույնը՝ նույնիսկ տարիներ անձրևի, ձյան և արևի ազդեցության տակ գտնվելուց հետո, ինչը նվազեցնում է հաճախադեպ վերաներկելու անհրաժեշտությունը: Ներքին ներկերը կիստածխածին են օգտագործում ակցենտավորված պատերի կամ դեկորատիվ ծածկույթների համար՝ ապահովելով հարուստ գույն, որը լավ է համատեղվում տարբեր դիզայնի ոճերի հետ: Ավտոմոբիլների վերանորոգման կամ արդյունաբերական հատակների համար օգտագործվող հատուկ լիցքավորումները կախված են կիստածխածնից՝ համապատասխան գույն և կատարողականություն ապահովելու համար: Ավտոմոբիլների վերանորոգման լիցքավորումները կիստածխածին են օգտագործում՝ սկզբնական գործարանային գույներին համապատասխանեցնելու համար և ապահովելու աննկատ վերանորոգումներ: Բարձր հարվածային ծանրության և քիմիկատների անջատումներին դիմադրող արդյունաբերական հատակների լիցքավորումները կիստածխածին են օգտագործում՝ տևականությունն ու սահքի դիմադրությունը բարելավելու համար:

Տպագրության ներկերի արդյունաբերությունը մոխրագույն ածխածնի մեկ այլ խոշոր օգտագործող է, որը գնահատվում է իր գունային ուժով, ցրման հատկություններով և լույսի նկատմամբ կայունությամբ: Լրագրերի տպագրության համար օգտագործվող ներկը կիրառում է մոխրագույն ածխածին՝ ապահովելու համար թղթի վրա հստակ և կարդալի տեքստ: Այս նյութը հավասարաչափ ցրվում է ներկի բաղադրություններում, ապահովելով համազոր ծածկույթ մեծ տպաքանակների դեպքում: Փաթեթավորման ներկերը, որոնք օգտագործվում են սննդի և սպառողական ապրանքների համար (ուտելիքի հետ անմիջական շփման բացառությամբ՝ համապատասխանելով սահմանափակումներին), օգտագործում են մոխրագույն ածխածին՝ ստեղծելու համար համարձակ էմբլեմներ և տեքստեր, որոնք դիմադրում են քսմանը և թուլացմանը: Այս ներկերը պետք է պահպանեն իրենց ամբողջականությունը տեղափոխման և պահեստավորման ընթացքում, իսկ մոխրագույն ածխածնի տևողականությունը ապահովում է, որ պիտակները մնան կարդալի: Արտադրության ընթացքում մասերի և բաղադրիչների նշման համար օգտագործվող արդյունաբերական նշման ներկերը կիրառում են մոխրագույն ածխածին՝ դիմադրություն ցուցաբերելու համար ճաքերի և քիմիական նյութերի նկատմամբ: Այս ներկերը ստեղծում են հավերժական նշումներ, որոնք դիմադրում են մշակմանը և փոխադրմանը, օգնելով պաշարների հետևումն ու որակի վերահսկումը: Հատուկ ներկերը, ինչպիսիք են ապահովության տպագրության կամ տեքստիլի տպագրության համար օգտագործվող ներկերը, օգտագործում են մոխրագույն ածխածին՝ օժտված լինելու համար որոշակի հատկություններով, ինչպիսիք են անթափանցելիությունը կամ հաղորդականությունը:
Ածխածին սևը արդյունաբերության այլ կիրառություններ է գտնում տարբեր ոլորտներում, որտեղ օգտագործվում են նրա յուրահատուկ հատկությունները: Բատարեաների արտադրության մեջ հաղորդակից տեսակի ածխածին սևը օգտագործվում է որպես էլեկտրոդային նյութերի ավելցուկ: Այս տեսակները բարելավում են էլեկտրոդների էլեկտրահաղորդականությունը, որն արդյունքում բարձրացնում է բատարեաների կատարողականությունն ու լիցքավորման արդյունավետությունը: Լիցքավորվող բատարեաները, որոնք օգտագործվում են սպառողական էլեկտրոնիկայում և էլեկտրական տրանսպորտային միջոցներում, շահում են ածխածին սևից՝ մեծացնելով էներգախտությունը և երկարաձգելով աշխատանքային ցիկլի կյանքը: Պատրաստաների և կպչուն նյութերի արդյունաբերություններում ածխածին սևը բարելավում է ճկունությունը, կպչունությունը և կայունությունը եղանակային պայմանների նկատմամբ: Շենքերում առաջացած ճեղքերը լցնելու համար օգտագործվող շինարարական պատրաստաները պարունակում են ածխածին սև՝ UV ճառագայթներից պաշտպանվելու և ջերմաստիճանային տատանումների դեպքում ճկունությունը պահպանելու համար: Արդյունաբերական կպչուն կառուցվածքներում օգտագործվող կպչուն նյութերը կիրառում են ածխածին սև՝ կապի ամրությունն ու կայունությունը բարելավելու համար: Բետոնի և շինարարական նյութերի մեջ ածխածին սևը օգտագործվում է որպես ներկանյութ դեկորատիվ բետոնե արտադրանքների համար, ինչպիսիք են հատակասալիկները, սալիկները և հատակապատումները: Այն տալիս է համազանգված սև գույն, որը կայուն է թափանցիկության նկատմամբ, որն էլ բարելավում է ճարտարապետական տարրերի էսթետիկ տեսքը: Ածխածին սևը նաև բարելավում է բետոնի կայունությունը՝ նվազեցնելով ճեղքերի առաջացումն ու կորցման մակարդակը ժամանակի ընթացքում:
Ածխածին սևը ստանալու համար կիրառվում են մի քանի մեթոդներ, որոնք նախատեսված են ստանալու հատուկ սեղանատեսակներ՝ տարբեր հատկություններով: Ամենատարածվածը հալացման սևի մեթոդն է, որն ընդգրկում է աշխարհի ամբողջ արտադրության մեծամասնությունը: Այս գործընթացի ընթացքում հեղուկ կամ գազային հիդրոկարբոններ են ներարկվում բարձր ջերմաստիճան ունեցող վառարանի մեջ, որտեղ տեղի է ունենում այրման անթերի պրոցես: Ստացված ածխածին սևը հավաքվում, սառեցվում և մշակվում է փոշու կամ փոքր կոկկոնների տեսքով: Հալացման սևի մեթոդն ապահովում է մասնիկների չափի և մակերեսի ճշգրիտ վերահսկողություն՝ արտադրելով սեղանատեսակներ, որոնք հարմար են կաուչուկի, պլաստմասսայի և ծածկույթների համար: Չանելային սևի մեթոդը, որը ավելի հին մեթոդ է, ներառում է բնական գազի անցկացումը տաքացված մետաղական չանելների վրայով, որտեղ ածխածին սևը նստում է չանելների մակերեսին: Այս մեթոդը արտադրում է փոքր մասնիկներ ունեցող ածխածին սև՝ բարձր ներկողականությամբ, որը հարմար է ծածկույթների և ներկերի համար: Ջերմային սևի մեթոդը օգտագործում է հիդրոկարբոնների ջերմային քայքայում՝ առանց թթվածնի, որի արդյունքում ստացվում է մեծ մասնիկներ ունեցող ածխածին սև՝ ցածր մակերեսով: Այս սեղանատեսակը կիրառվում է հաղորդակցություն կամ ցածր ամրացում պահանջող կիրառություններում, ինչպիսիք են պլաստմասսայե խողովակները և կաբելները: Յուրաքանչյուր արտադրական մեթոդ օպտիմալացված է էներգաօգտագործման և շրջակա միջավայրի վրա ազդեցության առումով, իսկ ժամանակակից սարքավորումները ներառում են արտանետումների վերահսկման համակարգեր՝ նվազեցնելու շրջակա միջավայրի վրա ունեցած ազդեցությունը:
Կարբոնային սևի արտադրության մեջ որակի վերահսկողությունը կարևոր է, քանի որ ապահովում է սեղանների ընդհանուր հատկությունների համաչափություն: Արտադրողները ամբողջ արտադրական գործընթացի ընթացքում իրականացնում են խիստ փորձարկումներ՝ հումքի ստուգումից սկսած մինչև վերջնական արտադրանքի վերլուծությունը: Հումքը, ինչպիսին են հիդրոկարբոնները, ստուգվում են մաքրության և համաչափության նկատմամբ, քանի որ խառնուրդները կարող են ազդել վերջնական կարբոնային սևի հատկությունների վրա: Արտադրության ընթացքում տարբեր փուլերում վերցվում են նմուշներ՝ հսկելու մասնիկների չափը, մակերեսի մակերեսը և կառուցվածքը: Մասնիկների չափը չափվում է հատուկ սարքավորումներով, որոնք վերլուծում են լույսի ցրման օրինակները՝ ապահովելով, որ մասնիկները համապատասխանեն նշված չափսերին: Մակերեսը որոշվում է ադսորբցման փորձարկումներով, որոնք չափում են կարբոնային սևի մակերեսին ադսորբված գազի քանակը: Կառուցվածքը, որը վերաբերում է մասնիկների ագրեգացման ձևին, գնահատվում է էլեկտրոնային մանրադիտակով և նստեցման փորձարկումներով: Վերջնական կարբոնային սևը ենթարկվում է լրացուցիչ փորձարկումների՝ կախված նախատեսված կիրառման տեսակից՝ ներառյալ գունային ուժի, ամրացման հատկությունների և հաղորդականության ստուգում: Այս փորձարկումները ապահովում են, որ կարբոնային սևը համապատասխանի արդյունաբերական ստանդարտներին և հաճախորդների պահանջներին՝ ապահովելով վստահելի աշխատանք վերջնական արտադրանքներում:
Կայունությունը ածխածին սևի արդյունաբերության հիմնական կետն է դարձել, որտեղ արտադրողները կիրառում են էկոլոգիապես մաքուր պրակտիկաներ՝ նվազեցնելու շրջակա միջավայրի վրա ունեցած ազդեցությունը: Էներգահամակարգի արդյունավետությունը առաջնահերթություն է, որտեղ ժամանակակից արտադրական սարքավորումները օգտագործում են թափոն ջերմությունը վերականգնելու համակարգեր՝ այրման ընթացքում առաջացած ջերմությունը վերահավաքելու և կրկին օգտագործելու համար: Այս ջերմությունը օգտագործվում է սարքավորման մյուս մասերը էներգամատակարարելու կամ էլեկտրաէներգիա արտադրելու համար, ինչը նվազեցնում է նավթային վառելիքների կախվածությունը: Մաքուր նյութերի կայունությունը մեկ այլ կենտրոնական ուշադրության առարկա է, որտեղ որոշ արտադրողներ հետազոտում են կենսածագման հումքային նյութեր, ինչպիսիք են բուսական յուղերը կամ գյուղատնտեսական թափոնները: Այս հումքային նյութերը նվազեցնում են նավթային հիդրոկարբոններից կախվածությունը և իջեցնում են ածխածնի արտանետումները: Արտանետման վերահսկման տեխնոլոգիաներ, ինչպիսիք են մաքրիչներն ու ֆիլտրները, օգտագործվում են ծծմբի երկօքսիդի և փոշու նման օդի աղտոտիչները նվազեցնելու համար: Օգտագործված ջրի մաքրման համակարգերն ապահովում են, որ արտադրության ընթացքում օգտագործված ջուրը մաքրվի և կրկին օգտագործվի կամ անցկացվի անվտանգ ձևով: Կրկնակի օգտագործումը և շրջանաձև տնտեսության պրակտիկաները նույնպես տարածված են դառնում՝ արտադրական գործընթացներից առաջացած ածխածնի սև թափոնները հավաքվում և կրկին օգտագործվում են ցածր տարբերակի կիրառություններում՝ թափոնները նվազեցնելու համար:
Ածխածին սևը շուկայի համաշխարհային շուկան շարժվում է տարբեր շրջանների արտադրական ոլորտների պահանջարկի շնորհիվ: Ասիա-Խաղաղօվկիանոսյան շրջանը ամենամեծ շուկան է, որը վառվում է Չինաստանի և Հնդկաստանի նման երկրներում ավտոմոտորային և շինարարական արդյունաբերության արագ աճի շնորհիվ: Այս շրջաններում ավտոմեքենաների արտադրության համար անհրաժեշտ են ածխածին սևի մեծ ծավալներ՝ ցենտրերի արտադրության համար, իսկ շինարարության ծաղկման շրջանում աճում է ածխածին սևի պահանջարկը պլաստմասսաների և ծածկույթների համար: Եվրոպան և Հյուսիսային Ամերիկան հասուն շուկաներ են, որտեղ պահանջարկը կենտրոնացած է էլեկտրական ավտոմեքենաների ցուպերի և առաջադեմ ծածկույթների նման հատուկ կիրառությունների համար նախատեսված բարձր կատարողականությամբ ածխածին սևի սերունդների վրա: Այս շրջանները նաև առաջնորդվում են ածխածին սևի կայուն սերունդներով, որոնք խթանում են էկոլոգիապես մաքուր արտադրության մեթոդների նորարարությունները: Լատինական Ամերիկան և Միջին Արևելքի Աֆրիկան արդյունաբերական շրջաններ են, որտեղ աճող արտադրական ոլորտները մեծացնում են ածխածին սևի պահանջարկը կաուչուկի և շինարարական նյութերի համար: Համաշխարհային մատակարարման շղթաները ապահովում են, որ ածխածին սևը արդյունավետ կերպով տրամադրվի հաճախորդներին ամբողջ աշխարհում, իսկ արտադրական հզորությունները գտնվում են խոշոր արտադրական կենտրոնների մոտ, որպեսզի նվազեցվեն տրանսպորտային ծախսերն ու առաքման ժամանակը:
Հաճախորդներին սպասարկումը և տեխնիկական սպասարկումը ածխածնային սև արտադրանքների արդյունաբերության մեջ հիմնարար դեր են խաղում, որտեղ արտադրողները սերտորեն համագործակցում են հաճախորդների հետ՝ բավարարելու նրանց կոնկրետ պահանջները: Տեխնիկական թիմերը փորձագիտական աջակցություն են ցուցաբերում յուրաքանչյուր կիրառման համար ճիշտ ածխածնային սև արտադրանքի տեսակը ընտրելու հարցում՝ հաշվի առնելով այնպիսի գործոններ, ինչպիսիք են կատարողականության պահանջները, արտադրական գործընթացները և ծախսային սահմանափակումները: Օրինակ՝ էլեկտրական տրանսպորտային միջոցների համար բարձր կատարողականության անվադողեր մշակող արտադրողը կարող է ուղղորդվել ածխածնային սև արտադրանքի այն տեսակները ընտրելու հարցում, որոնք ապահովում են ավելի մեծ մաշվածականություն և նվազեցնում են անվադողերի դիմադրությունը գլորման ժամանակ: Կարելի է օգտագործել հատուկ ձևավորված բաղադրատոմսեր հաճախորդների համար, ովքեր ունեն յուրահատուկ պահանջներ, ինչպիսիք են հատուկ ներկապատվածքները՝ որոնք պահանջում են կոնկրետ գունավորման ուժ կամ էլեկտրահաղորդականություն: Արտադրողները նաև տրամադրում են վերապատրաստումներ և ռեսուրսներ՝ օգնելու հաճախորդներին ածխածնային սև արտադրանքի օպտիմալ օգտագործման հարցում, ներառյալ խառնման հանձնարարականներ և որակի վերահսկման կանոնակարգեր: Վաճառքից հետո աջակցությունը ապահովում է, որ ցանկացած խնդիր արագ լուծվի՝ նվազագույնի հասցնելով հաճախորդների արտադրական կանգները: Այս համագործակցային մոտեցումը նպաստում է ածխածնային սև արտադրանքների արտադրողների և նրանց հաճախորդների միջև երկարաժամկետ գործընկերությունների ձևավորմանը:
 ×
×