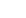
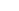
Sphagnum moss, commonly known as peat moss or water moss, is a genus of bryophytes with significant ecological and practical importance. These plants typically grow in wetland areas, such as bogs and swamps, where they form dense mats.
Ecologically, sphagnum moss plays a crucial role in wetland ecosystems. It helps maintain the water balance in bogs by retaining water during rainy periods and slowly releasing it during dry spells. It also provides habitats for a variety of microorganisms, insects, and small animals. Moreover, as sphagnum decomposes very slowly in the acidic and water - logged conditions of bogs, it accumulates over time and contributes to the formation of peat, which is an important carbon sink on Earth.
In practical applications, water moss is widely used in horticulture. It is an ideal growing medium for many plants, especially those that prefer acidic and well - drained but moisture - retentive conditions, such as orchids, carnivorous plants, and some ferns. Sphagnum can be used alone or mixed with other substrates like perlite or bark. It also serves as a covering material for plant cuttings, helping to keep them moist and promoting root formation. Additionally, in the florist industry, sphagnum is used to wrap flower stems to keep them hydrated during transportation.
 ×
×